Performance Benchmarks
Let’s shift our focus to the performance benchmarks, where real-world scenarios and synthetic tests will shed light on how these architectural disparities translate into tangible computing power. By analyzing their performance across multiple benchmarks, we can comprehensively understand how these chips stack up against each other.
Cinebench R23 (Single-Core)
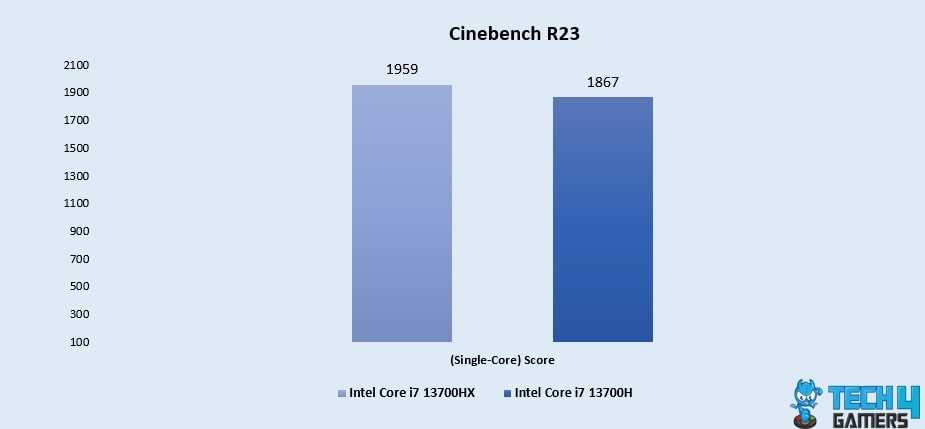
Cinebench R23 (Single-Core) Performance Benchmarks – Image Credits (Tech4Gamers)
Firstly, the Core i7 13700HX boasts a 4.8% lead over the Core i7 13700H, with scores of 1959 and 1867, respectively. This performance differential indicates the Core i7 13700HX’s potential for swift and efficient execution of single-core tasks.
Cinebench R23 (Multi-Core)

Cinebench R23 (Multi-Core) Performance Benchmarks – Image Credits (Tech4Gamers)
In multi-core performance, the Core i7 13700HX takes a substantial 32.5% lead, achieving scores of 22777 compared to the Core i7 13700H’s 16402. This advantage highlights the Core i7 13700HX’s efficiency in managing demanding workloads.
Geekbench 5 (Single-Core)

Geekbench 5 (Single-Core) Performance Benchmarks – Image Credits (Tech4Gamers)
With a 1.5% lead in single-core benchmarks, the Core i7 13700H achieves a score of 1901, slightly trailing behind the Core i7 13700HX’s score of 1871. This nuanced difference indicates varying single-threaded processing capabilities.
Geekbench 5 (Multi-Core)
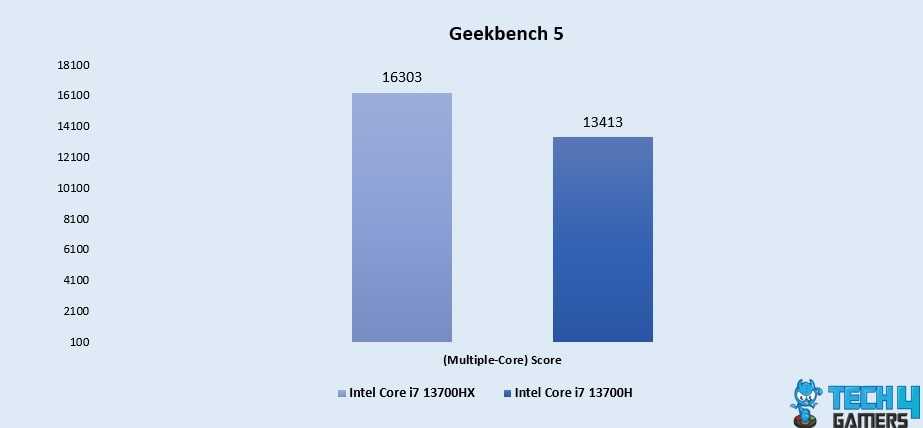
Geekbench 5 (Multi-Core) Performance Benchmarks – Image Credits (Tech4Gamers)
Finally, the Core i7 13700HX maintains a notable 19.4% lead in multi-core benchmarks, scoring 16303, while the Core i7 13700H achieves 13413. This distinction underscores the Core i7 13700HX’s proficiency in handling complex multi-threaded tasks.
Similar Comparisons: Core i7 13700H Vs Core i7 12700H
Download Uniwill 259IA3 BIOS 1.09 driver
Uniwill 259IA3 BIOS 1.09
The operating system should automatically install the appropriate driver Uniwill 259IA3 BIOS 1.09 to your Uniwill device. If this has not happened, without a manual Uniwill 259IA3 BIOS 1.09 driver installation your device may not work properly or may not use all of its features. Download the Uniwill 259IA3 BIOS 1.09 driver and install it on your computer — if the device still is not working properly, read the information further down the site about the Uniwill device from the BIOS category. There you will find helpful tips on how to install the Uniwill 259IA3 BIOS 1.09 driver. You will also learn why it is so important to have current Uniwill drivers.
Driver details
| Operating System | / Windows 9X / ME / NT / 2K / XP / 2003 / Vista / XP 64 bit / 2008 / Vista 64 bit / 7 / 7 64 bit / 8 / 8 64 bit / Android / Server 2012 / OS Independent / 8.1 / 8.1 64 bit / 10 / 10 64 bit / Li | |
| File size | 978 MB | |
| Category: | Uniwill • BIOS | |
| Number of downloads | 1326 | |
| Last update /Date added | 25.07.2014 |
My device has not been properly installed — what should I do?
After connecting a new Uniwill device to your computer, the system should automatically install the Uniwill 259IA3 BIOS 1.09 driver. If this has not happened, you should take the following steps: 1. Check if the automatic update is enabled
It is the automatic update feature that is responsible for the installation of the BIOS Uniwill drivers on your computer. If the «UPDATE» feature was disabled, the Uniwill 259IA3 BIOS 1.09 driver could not be installed. It is worth noting that in order for the automatic update to work, the computer must be connected to the Internet (perhaps when connecting the Uniwill device the computer temporarily did not have the Internet connection or a WiFi signal was weak making it impossible to download the Uniwill 259IA3 BIOS 1.09 driver). To make sure, disconnect now and reconnect the Uniwill device again, and maybe this time the driver will be downloaded.
2. Install the driver manually
This solution may seem more complicated — but it is nothing further from the truth. Just download the Uniwill 259IA3 BIOS 1.09 driver and start the installation (keeping in mind that the Uniwill device must be at the same time connected to the computer). After the installation of the Uniwill 259IA3 BIOS 1.09 driver, the device should work properly.
The update of the Uniwill device driver which is not working properly
It is very important that the Uniwill devices connected to your computer had their current drivers installed. Without current Uniwill 259IA3 BIOS 1.09 drivers there is a greater risk of the device malfunction, of the reduction in security, and there is a possibility of the total damage of the Uniwill device. Manufacturers from time to time issue new versions of the Uniwill 259IA3 BIOS 1.09 software, repairing the errors they find that may cause problems with the Uniwill devices. Therefore, if you notice that a new version of the Uniwill 259IA3 BIOS 1.09 driver is available, you should install it immediately.
Similar drivers from the Uniwill category
| Driver name | Driver details |
|---|---|
| Uniwill L51II BIOS 1.10 | 513 MB / Windows 9X / ME / NT / 2K / XP / 2003 / Vista / XP 64 bit / 2008 / Vista 64 bit / 7 / 7 64 bit / 8 / 8 64 bit / Android / Server 2012 / OS Independent / 8.1 / 8.1 64 bit / 10 / 10 64 bit / Li |
| Uniwill L51AI BIOS 1.02 | 512 MB / Windows 9X / ME / NT / 2K / XP / 2003 / Vista / XP 64 bit / 2008 / Vista 64 bit / 7 / 7 64 bit / 8 / 8 64 bit / Android / Server 2012 / OS Independent / 8.1 / 8.1 64 bit / 10 / 10 64 bit / Li |
| Uniwill M31EI BIOS 1.05 | 512 MB / Windows 9X / ME / NT / 2K / XP / 2003 / Vista / XP 64 bit / 2008 / Vista 64 bit / 7 / 7 64 bit / 8 / 8 64 bit / Android / Server 2012 / OS Independent / 8.1 / 8.1 64 bit / 10 / 10 64 bit / Li |
| Uniwill 223ii0 BIOS 1.10 | 420 MB / Windows 9X / ME / NT / 2K / XP / 2003 / Vista / XP 64 bit / 2008 / Vista 64 bit / 7 / 7 64 bit / 8 / 8 64 bit / Android / Server 2012 / OS Independent / 8.1 / 8.1 64 bit / 10 / 10 64 bit / Li |
| Uniwill 259IA3 BIOS 1.09 | 978 MB / Windows 9X / ME / NT / 2K / XP / 2003 / Vista / XP 64 bit / 2008 / Vista 64 bit / 7 / 7 64 bit / 8 / 8 64 bit / Android / Server 2012 / OS Independent / 8.1 / 8.1 64 bit / 10 / 10 64 bit / Li |
| Show all drivers by BIOS Uniwill |
| Choose language |
|---|
| Uniwill 259IA3 BIOS 1.09 driver |
| Driver Uniwill 259IA3 BIOS 1.09 |
| Sterowniki Uniwill 259IA3 BIOS 1.09 |
| Uniwill 259IA3 BIOS 1.09 treiber |
| Uniwill 259IA3 BIOS 1.09ドライバ |
| Pilotes Uniwill 259IA3 BIOS 1.09 |
Intel Mobility CPU Lineup:
| CPU Family | Lunar Lake | Arrow Lake | Meteor Lake | Raptor Lake | Alder Lake |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Process Node (CPU Tile) | Intel 20A? | Intel 20A ‘5nm EUV» | Intel 4 ‘7nm EUV’ | Intel 7 ’10nm ESF’ | Intel 7 ’10nm ESF’ |
| Process Node (GPU Tile) | TSMC 3nm? | TSMC 3nm | TSMC 5nm | Intel 7 ’10nm ESF’ | Intel 7 ’10nm ESF’ |
| CPU Architecture | Hybrid | Hybrid (Four-Core) | Hybrid (Triple-Core) | Hybrid (Dual-Core) | Hybrid (Dual-Core) |
| P-Core Architecture | Lion Cove? | Lion Cove | Redwood Cove | Raptor Cove | Golden Cove |
| E-Core Architecture | Skymont? | Skymont | Crestmont | Gracemont | Gracemont |
| LP E-Core Architecture (SOC) | Skymont? | Crestmont? | Crestmont? | N/A | N/A |
| Top Configuration | TBD | TBD | 6+8 (H-Series) | 6+8 (H-Series) 8+16 (HX-Series) |
6+8 (H-Series) 8+8 (HX-Series) |
| Max Cores / Threads | TBD | TBD | 14/20 | 14/20 | 14/20 |
| Planned Lineup | U Series? | H/P/U Series | H/P/U Series | H/P/U Series | H/P/U Series |
| GPU Architecture | Xe2-LPG (Battlemage) | Xe-LPG (Alchemist) | Xe-LPG (Alchemist) | Iris Xe (Gen 12) | Iris Xe (Gen 12) |
| GPU Execution Units | 64 EUs | 192 EUs | 128 EUs (1024 Cores) | 96 EUs (768 Cores) | 96 EUs (768 Cores) |
| Memory Support | TBD | TBD | DDR5-5600 LPDDR5-7400 LPDDR5X — 7400+ |
DDR5-5200 LPDDR5-5200 LPDDR5-6400 |
DDR5-4800 LPDDR5-5200 LPDDR5X-4267 |
| Memory Capacity (Max) | TBD | TBD | 96 GB | 64 GB | 64 GB |
| Thunderbolt 4 Ports | TBD | TBD | 4 | 4 | 4 |
| WiFi Capability | TBD | TBD | WiFi 6E | WiFi 6E | WiFi 6E |
| TDP | TBD | TBD | 7W-45W | 15-55W | 15-55W |
| Launch | 2H 2024 | 2H 2024 | 2H 2023 | 1H 2023 | 1H 2022 |
News Source: Benchleaks
Core i7 13700H Vs Core i7 13700HX: Which One Should You Go For?
- The Core i7 13700HX holds a slight 1.6% advantage in single-core benchmarks, showcasing its capability for efficient execution of individual tasks and applications, making it a favorable choice for users seeking quick responsiveness.
- Moreover, using a substantial 26.8% lead in multi-core benchmarks, the Core i7 13700HX emerges as the preferred option for resource-intensive workloads and multitasking scenarios, ensuring smoother performance in demanding computing tasks.
- While both chips offer configurable TDPs, the Core i7 13700H features a range of 35-45W, whereas the Core i7 13700HX offers a slightly broader range of 45-55W. This adaptability allows users to prioritize performance or power efficiency.
- The Core i7 13700HX supports a higher memory capacity of up to 128GB, making it well-suited for memory-intensive apps. Its ECC memory support also provides enhanced accuracy, which is absent in the Core i7 13700H, which supports up to 64GB of memory.
FAQs
What is the primary difference between the Core i7 13700HX and Core i7 13700H in terms of performance?
The Core i7 13700HX exhibits better multi-core performance with a significant 39% lead in multi-core benchmarks.
How does the memory support of Core i7 13700HX and Core i7 13700H differ?
The Core i7 13700HX supports up to 128GB of memory, offering ample room for memory-intensive applications, while the Core i7 13700H supports up to 64GB.
Which CPU provides better power management options, Core i7 13700HX or Core i7 13700H?
Both processors offer configurable TDPs, but the Core i7 13700HX offers a slightly broader range of 45-55W, giving users more flexibility to balance performance.
Was our article helpful?
Yes
No
Thank you! Please share your positive feedback.
How could we improve this post? Please Help us.
Specifications:
| Processor | Intel Core i7-13700HX | |||
| Market (main) | Laptop | |||
| ISA | x86-64 (64 bit) | |||
| Microarchitecture | Raptor Cove + Gracemont | |||
| Core name | Raptor Lake-HX | |||
| Family | Core i7-13000 | |||
| Part number(s), S-Spec |
CM8071505105534, CM8071505248804, SRME5, SRMLH |
|||
| Release date | Q1 2023 | |||
| Lithography | Intel 7 | |||
| Cores | 16 | |||
| Threads | 24 | |||
| Base frequency | 2.1 GHz | |||
| Turbo frequency | 5.0 GHz | |||
| Energy cores | 8 Cores 8 Threads @ 1.5 / 3.7 GHz | |||
| High performance cores | 8 Cores 16 Threads @ 2.1 / 5.0 GHz | |||
| Cache memory | 30 MB | |||
| Max memory capacity | 192 GB | |||
| Memory types | DDR5 4800 MT/s, DDR4 3200 MT/s | |||
| Max # of memory channels | 2 | |||
| Max memory bandwidth | 76.8 GB/s | |||
| Max PCIe lanes | 20 | |||
| TDP | 55 W | |||
| GPU integrated graphics | Intel UHD Graphics 770 (Raptor Lake) | |||
| GPU execution units | 32 | |||
| GPU shading units | 256 | |||
| GPU base clock | 300 MHz | |||
| GPU boost clock | 1,550 MHz | |||
| GPU FP32 floating point | 844.8 GFLOPS | |||
| Socket | BGA1964 | |||
| Maximum temperature | 100°C | |||
| AI accelerator |
Gaussian & Neural Accelerator, Deep Learning Boost |
|||
| Crypto engine |
AES New Instructions, Secure Key |
|||
| Security |
OS Guard, Boot Guard |
|||
| Max display resolution |
4096 x 2160@60Hz (HDMI), 7680 x 4320@60Hz (DP), 5120 x 3200@120Hz (eDP) |
|||
| CPU-Z single thread | 780 | |||
| CPU-Z multi thread | 9,863 | |||
| Cinebench R15 single thread | 259 | |||
| Cinebench R15 multi-thread | 3,303 | |||
| Cinebench R20 single thread | 693 | |||
| Cinebench R20 multi-thread | 7,832 | |||
| Cinebench R23 single thread | 1,750 | |||
| Cinebench R23 multi-thread | 20,297 | |||
| PassMark single thread | 4,015 | |||
| PassMark CPU Mark | 31,972 | |||
| (Windows)Geekbench 4 single core | 6,413 | |||
| (Windows)Geekbench 4 multi-core | 45,160 | |||
| (Windows)Geekbench 5 single core | 1,844 | |||
| (Windows)Geekbench 5 multi-core | 14,163 | |||
| (Windows)Geekbench 6 single core | 2,570 | |||
| (Windows)Geekbench 6 multi-core | 14,156 | |||
| (SGEMM)GFLOPS Performance | 796 GFLOPS | |||
| (Multi-core / watt performance)Performance / watt ratio | 821 pts / W | |||
| Amazon | ||||
| eBay |
Core i7 13700HX Vs Core i7 13700H: Architectural Differences
As we delve into the architectural differences between the Core i7 13700HX and Core i7 13700H, it becomes evident that these two processors share a common foundation while offering distinct variations that impact their performance capabilities.
- Process Node: Firstly, while both the Core i7 13700HX and Core i7 13700H share a 10nm process node, their performance implications vary due to other architectural factors.
- Clock Speed: Furthermore, the Core i7 13700HX features a Base Clock of 2.1 GHz and a Boost Clock of 5 GHz, offering competitive performance. In comparison, the Core i7 13700H operates with a slightly higher Base Clock of 2.4 GHz and the same Boost Clock of 5 GHz, potentially influencing its efficiency.
- Memory Support Variation: The Core i7 13700HX provides an expansive memory capacity of up to 128GB, catering to memory-intensive tasks. On the other hand, the Core i7 13700H supports up to 64GB.
- TDP: While the Core i7 13700HX and Core i7 13700H both offer configurable TDPs for power management, the former comes with a range of 45-55W, potentially providing more headroom for applications, whereas the latter offers a range of 35-45W.
- Supported Technologies: The Core i7 13700HX stands out with its support for ECC memory, a valuable feature for enhanced error correction in critical computing tasks. However, the Core i7 13700H lacks this technology.
Also Check: Core i7 1360P Vs Core i7 13700H
Performance
CPU speed
8 x 2.1 GHz & 8 x 1.5 GHz
The CPU speed indicates how many processing cycles per second can be executed by a CPU, considering all of its cores (processing units). It is calculated by adding the clock rates of each core or, in the case of multi-core processors employing different microarchitectures, of each group of cores.
CPU threads
24 threads
More threads result in faster performance and better multitasking.
turbo clock speed
5GHz
When the CPU is running below its limitations, it can boost to a higher clock speed in order to give increased performance.
Has an unlocked multiplier
Intel Core i7-13700HX
Some processors come with an unlocked multiplier which makes them easy to overclock, allowing you to gain increased performance in games and other apps.
L2 cache
24 MB
A larger L2 cache results in faster CPU and system-wide performance.
L3 cache
30 MB
A larger L3 cache results in faster CPU and system-wide performance.
L1 cache
Unknown. Help us by suggesting a value.
A larger L1 cache results in faster CPU and system-wide performance.
L2 core
Unknown. Help us by suggesting a value.
More data can be stored in the L2 cache for access by each core of the CPU.
L3 core
Unknown. Help us by suggesting a value.
More data can be stored in the L3 cache for access by each core of the CPU.
General info
Type
Laptop
The market that the CPU is designed for.
CPU socket
Unknown. Help us by suggesting a value.
The CPU socket/s supported.
Chipset
Unknown. Help us by suggesting a value.
The motherboard chipset/s supported.
Has integrated graphics
Intel Core i7-13700HX
With integrated graphics you don’t need to buy a separate graphics card.
semiconductor size
10 nm
Small semiconductors provide better performance and reduced power consumption. Chipsets with a higher number of transistors, semiconductor components of electronic devices, offer more computational power. A small form factor allows more transistors to fit on a chip, therefore increasing its performance.
Thermal Design Power (TDP)
55W
The thermal design power (TDP) is the maximum amount of power the cooling system needs to dissipate. A lower TDP typically means that it consumes less power.
CPU temperature
100 °C
If the CPU exceeds the maximum operating temperature then problems such as random resets can occur.
PCI Express (PCIe) version
5
Peripheral Component Interconnect Express (PCIe) is a high-speed interface standard for connecting components, such as graphics cards and SSDs, to a motherboard. Newer versions can support more bandwidth and deliver better performance.
number of transistors
Unknown. Help us by suggesting a value.
A higher transistor count generally indicates a newer, more powerful processor.
Integrated graphics
GPU clock speed
300 MHz
The clock speed of the graphics processing unit (GPU).
GPU turbo
1600 MHz
When the GPU is running below its limitations, it can boost to a higher clock speed in order to give increased performance.
GPU execution units
32
A graphics processing unit (GPU) with a greater number of execution units can deliver better graphics.
DirectX version
DirectX 12
DirectX is used in video games, with newer versions supporting better graphics and features. The latest version is DirectX 12 Ultimate, which includes support for ray tracing, mesh shaders, and variable rate shading (VRS).
supported displays
4
Using multiple displays you can create a larger workspace, making it easier to work across multiple apps.
OpenGL version
4.6
OpenGL is used in games, with newer versions supporting better graphics.
OpenCL version
3
Some apps use OpenCL to apply the power of the graphics processing unit (GPU) for non-graphical computing. Newer versions introduce more functionality and better performance.
texture mapping units (TMUs)
16
TMUs take textures and map them to the geometry of a 3D scene. More TMUs will typically mean that texture information is processed faster.
render output units (ROPs)
8
The ROPs are responsible for some of the final steps of the rendering process, writing the final pixel data to memory and carrying out other tasks such as anti-aliasing to improve the look of graphics.
Intel Core i7-13700HX ‘Raptor Lake’ High-End Laptop CPU Rocks 16 Cores & Up To 5.0 GHz Clocks
The Intel Core i7-13700HX ‘Raptor Lake’ CPU will be part of the high-end 13th Gen Laptop CPU line. The HX series utilize the same die as the desktop Raptor Lake-S parts so we will also be looking at a similar set of core configurations.
In the case of the Intel Core i7-13700HX, we are getting 16 cores using a 8 P-Core & 8 E-Core layout. This equals to a total of 24 threads which is the same configuration as the current Core i7-13700K or the last-gen Core i9-12900K/KS flagships. The CPU features 30 MB of L3 cache and was seen on the Lenovo 82WQ laptop with 16 GB of DDR5 memory. The CPU featured a 2.10 GHz base clock and boost clocks of up to 5.0 GHz.
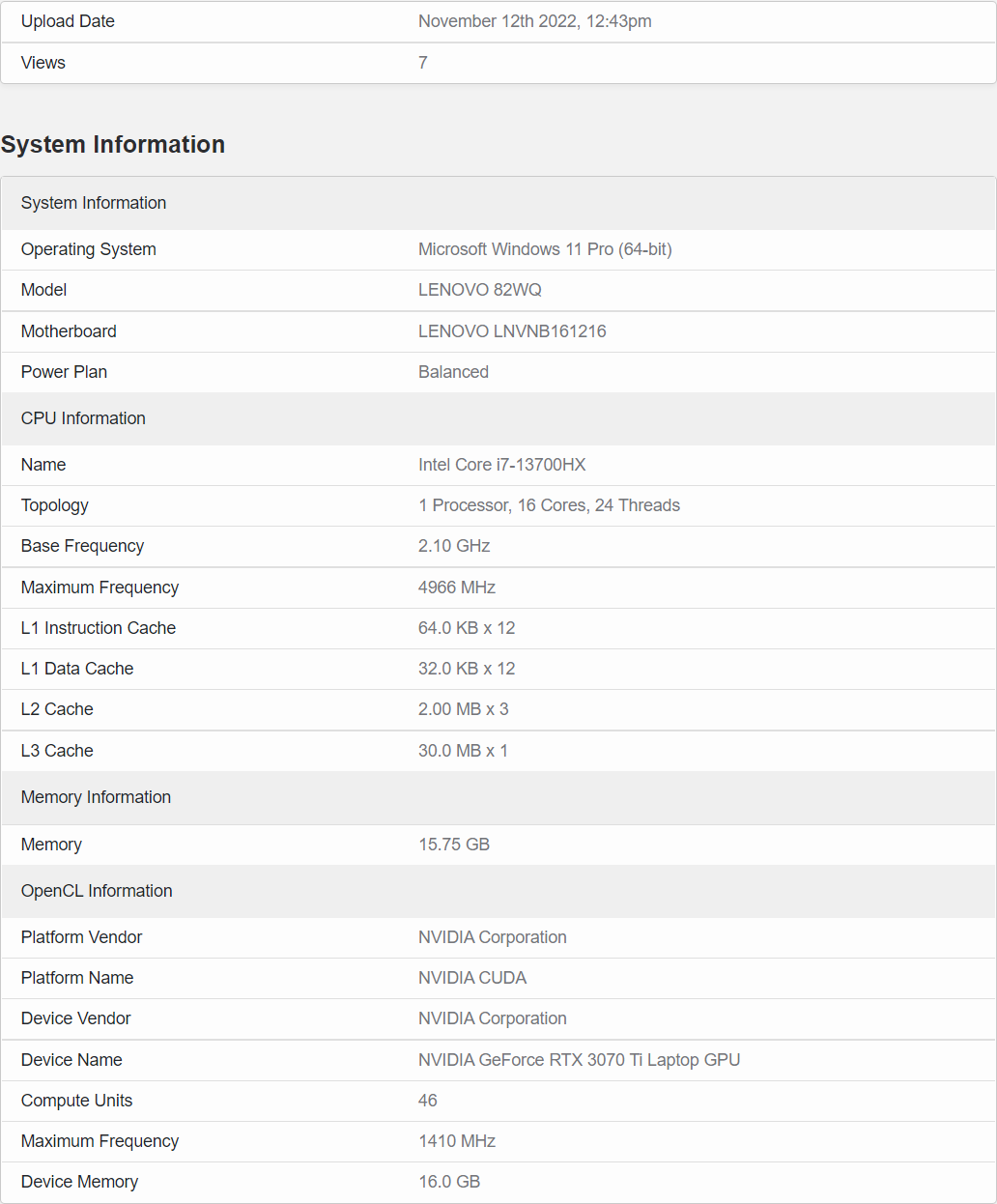
Intel’s 16-Core Raptor Lake-HX chip, the Core i7-13700HX, has leaked out and features up to 5.0 GHz clock speeds. (Image Credits: Benchleaks)
Uniwill specs
Uniwill is based on 16-cores CPU Intel Core i7-13700HX. CPU TDP of Uniwill is 122 watts, which is a typical characteristic of a powerful processor. When the load is above average, you will not be able to move away from the outlet. NVIDIA GeForce RTX 4070 Laptop GPU is responsible for the graphics. Add to the CPU power 140 W of graphics adapter, and at maximum performance you can only work fully from the power supply.
Uniwill has 32 GB 2-channel RAM DDR5. This is enough not only for the most modern games, but also for video editing and other resource-intensive activities.
In our configuration, a fast SSD Samsung PM9A1 MZVL2512HCJQ with a volume of 512 GB is presented as storage. SSD capacity is enough for most tasks, however, if you are interested in video production or modern games, 512 GB may not be enough.
Benchmarks
PassMark result
31983
This benchmark measures the performance of the CPU using multiple threads.
PassMark result (single)
4006
This benchmark measures the performance of the CPU using a single thread.
Cinebench R20 (multi) result
8342
Cinebench R20 is a benchmark tool that measures a CPU’s multi-core performance by rendering a 3D scene.
Cinebench R20 (single) result
734
Cinebench R20 is a benchmark tool that measures a CPU’s single-core performance by rendering a 3D scene.
Geekbench 6 result (multi)
Unknown. Help us by suggesting a value.
Geekbench 6 is a cross-platform benchmark that measures a processor’s multi-core performance. (Source: Primate Labs, 2024)
Geekbench 6 result (single)
Unknown. Help us by suggesting a value.
Geekbench 6 is a cross-platform benchmark that measures a processor’s single-core performance. (Source: Primate Labs, 2024)
Geekbench 5 result (multi)
Unknown. Help us by suggesting a value.
Geekbench 5 is a cross-platform benchmark that measures a processor’s multi-core performance. (Source: Primate Labs, 2024)
Geekbench 5 result (single)
Unknown. Help us by suggesting a value.
Geekbench 5 is a cross-platform benchmark that measures a processor’s single-core performance. (Source: Primate Labs, 2024)
Blender (bmw27) result
Unknown. Help us by suggesting a value.
The Blender (bmw27) benchmark measures the performance of a processor by rendering a 3D scene. More powerful processors can render the scene in less time.
Performance with the benchmarks:
| CPU-Z — Multi-Thread & Single Thread Score | |
|---|---|
| AMD Ryzen 9 7945HX | 73313,934 |
| AMD Ryzen 9 7945HX3D | 68213,880 |
| Intel Core i9-14900HX | 84513,734 |
| Intel Core i9-13950HX | 88213,025 |
| AMD Ryzen 9 7845HX | 71210,486 |
| Intel Core i7-13700HX | 7809,863 |
| Intel Core i9-13900HX | 4429,448 |
| Intel Core i9-12900HX | 7199,446 |
| Intel Core i7-12850HX | 7429,180 |
| Intel Core i9-12950HX | 7409,177 |
| Cinebench R15 — Multi-Thread & Single Thread Score | |
|---|---|
| Intel Core i9-13950HX | 3054,517 |
| AMD Ryzen 9 7845HX | 2944,363 |
| Intel Core i9-12900HX | 2833,589 |
| Apple M3 Max 16-Core | 2723,433 |
| Intel Core i7-12800HX | 2513,378 |
| Intel Core i7-13700HX | 2593,303 |
| Intel Core i7-13650HX | 2783,155 |
| Intel Core i9-12950HX | 2803,126 |
| Intel Core i9-13900H | 2773,044 |
| Intel Core i9-13900HK | 2842,963 |
| Cinebench R20 — Multi-Thread & Single Thread Score | |
|---|---|
| AMD Ryzen 9 7845HX | 70710,516 |
| Intel Core i9-12900HX | 7498,866 |
| Intel Core i7-12800HX | 6638,552 |
| Intel Core i7-13650HX | 7198,008 |
| Intel Core i9-12950HX | 7187,939 |
| Intel Core i7-13700HX | 6937,832 |
| Intel Core Ultra 9 185H | 7007,700 |
| Intel Core i9-13900HK | 7547,563 |
| Intel Core i9-13900H | 7307,388 |
| AMD Ryzen 7 7745HX | 7337,134 |
| Cinebench R23 — Multi-Thread & Single Thread Score | |
|---|---|
| Apple M3 Max 16-Core | 1,97323,983 |
| Intel Core i9-12900HX | 1,89723,173 |
| Intel Core i7-12800HX | 1,82522,433 |
| Intel Core i7-13650HX | 1,89121,024 |
| Intel Core i9-12950HX | 1,87320,374 |
| Intel Core i7-13700HX | 1,75020,297 |
| Intel Core i9-13900HK | 1,98219,625 |
| Intel Core i9-13900H | 1,92519,557 |
| AMD Ryzen 7 7745HX | 1,85418,325 |
| Intel Core i9-12900HK | 1,89818,266 |
| PassMark — CPU Mark | |
|---|---|
| Intel Core Ultra 9 185H | 3,99733,288 |
| Intel Core i7-13650HX | 3,83933,023 |
| AMD Ryzen 7 7745HX | 3,86232,934 |
| Intel Core i9-12900H | 3,93732,472 |
| Intel Core i9-13900H | 4,04232,224 |
| Intel Core i7-13700HX | 4,01531,972 |
| Intel Core i9-13905H | 3,93331,715 |
| Intel Core Ultra 7 165H | 3,87331,607 |
| Intel Core i9-12900HX | 4,02231,067 |
| AMD Ryzen 9 7940H | 4,05130,892 |
With Windows:
| Geekbench 4 — Multi-core & Single Core Score — Windows | |
|---|---|
| AMD Ryzen 9 PRO 7940HS | 7,89248,407 |
| Intel Core i7-12850HX | 7,68147,347 |
| Intel Core i9-12900H | 7,90447,180 |
| AMD Ryzen 9 7940HS | 8,12547,176 |
| AMD Ryzen 7 7840HS | 7,92645,518 |
| Intel Core i7-13700HX | 6,41345,160 |
| Intel Core i7-12800H | 7,40845,107 |
| Intel Core i7-13620H | 8,13844,929 |
| AMD Ryzen 7 7840H | 8,12544,632 |
| AMD Ryzen 7 PRO 7840HS | 7,32044,234 |
With Windows:
| Geekbench 5 — Multi-core & Single Core Score — Windows | |
|---|---|
| Intel Core i9-12900HX | 1,62115,592 |
| Intel Core i7-13800H | 1,84514,464 |
| Intel Core i9-12950HX | 1,62014,463 |
| Intel Core i7-14650HX | 1,96414,326 |
| Intel Core i5-13600HX | 1,86514,295 |
| Intel Core i7-13700HX | 1,84414,163 |
| Intel Core i7-12800HX | 1,71414,112 |
| Intel Core i9-12900HK | 1,80714,057 |
| Intel Core i7-12850HX | 1,75413,726 |
| Intel Core i9-13900HK | 1,97613,726 |
With Linux:
| Geekbench 5 — Multi-core & Single Core Score — Linux | |
|---|---|
| AMD Ryzen 9 7945HX3D | 2,26021,856 |
| AMD Ryzen 9 7945HX | 2,10121,364 |
| Intel Core i9-13950HX | 2,11320,527 |
| Intel Core i9-13900HX | 2,07419,756 |
| Intel Core i9-13980HX | 2,15019,136 |
| Intel Core i7-13700HX | 2,09017,477 |
| Intel Core i9-12900HX | 2,02915,663 |
| AMD Ryzen 9 7845HX | 2,11515,222 |
| Intel Core i9-13905H | 2,08115,133 |
| Intel Core i9-12950HX | 1,90914,885 |
With Android:
| Geekbench 5 — Multi-core & Single Core Score — Android | |
|---|---|
| AMD Ryzen 9 7945HX3D | 1,55714,846 |
| AMD Ryzen 9 7945HX | 1,32013,583 |
| Intel Core i9-13900HX | 2,18813,411 |
| Intel Core i7-13700HX | 1,58412,067 |
| Intel Core i9-12900H | 1,58011,388 |
| Intel Core Ultra 7 155H | 1,49911,213 |
| Intel Core i9-12950HX | 1,50510,856 |
| AMD Ryzen 9 7940H | 1,4059,587 |
With Windows:
| Geekbench 6 — Multi-core & Single Core Score — Windows | |
|---|---|
| AMD Ryzen 9 7845HX | 2,80015,353 |
| Intel Core i9-12900HX | 2,53315,229 |
| Intel Core i9-13905H | 2,76414,783 |
| Intel Core i9-13900HK | 2,67214,705 |
| Intel Core i9-12950HX | 2,49614,462 |
| Intel Core i7-13700HX | 2,57014,156 |
| Intel Core i5-13600HX | 2,45114,140 |
| Intel Core i7-12800HX | 2,47714,094 |
| AMD Ryzen 7 7745HX | 2,78413,921 |
| AMD Ryzen 9 7940HS | 2,67513,823 |
With Linux:
| Geekbench 6 — Multi-core & Single Core Score — Linux | |
|---|---|
| Intel Core i7-13850HX | 2,94417,084 |
| Intel Core i9-13980HX | 2,94216,452 |
| AMD Ryzen 9 7845HX | 2,79116,246 |
| Intel Core i9-12900HX | 2,76315,389 |
| Intel Core i7-14650HX | 2,16814,551 |
| Intel Core i7-13700HX | 2,63614,476 |
| AMD Ryzen 7 7745HX | 2,78514,379 |
| Intel Core i9-12950HX | 2,23514,226 |
| Intel Core i7-12800HX | 2,57114,197 |
| Intel Core i7-13700H | 2,67713,875 |
List of comparisons:
AMDAMD A10AMD A12AMD A4AMD A6AMD A8AMD A9AMD AthlonAMD Athlon 64AMD Athlon 64 X2AMD Athlon GoldAMD Athlon IIAMD Athlon SilverAMD Athlon X2AMD EPYCAMD FXAMD JaguarAMD OpteronAMD PhenomAMD RyzenAMD Ryzen 1000AMD Ryzen 2000AMD Ryzen 3AMD Ryzen 3 1000AMD Ryzen 3 2000AMD Ryzen 3 3000AMD Ryzen 3 4000AMD Ryzen 3 5000AMD Ryzen 3 MobileAMD Ryzen 3000AMD Ryzen 4000AMD Ryzen 5AMD Ryzen 5 1000AMD Ryzen 5 2000AMD Ryzen 5 3000AMD Ryzen 5 4000AMD Ryzen 5 5000AMD Ryzen 5 6000 MobileAMD Ryzen 5 7000AMD Ryzen 5 MobileAMD Ryzen 5000AMD Ryzen 6000 MobileAMD Ryzen 7AMD Ryzen 7 1000AMD Ryzen 7 2000AMD Ryzen 7 3000AMD Ryzen 7 4000AMD Ryzen 7 5000AMD Ryzen 7 6000 MobileAMD Ryzen 7 7000AMD Ryzen 7 MobileAMD Ryzen 7000AMD Ryzen 8000AMD Ryzen 9AMD Ryzen 9 3000AMD Ryzen 9 4000AMD Ryzen 9 5000AMD Ryzen 9 6000 MobileAMD Ryzen 9 7000AMD Ryzen 9 MobileAMD Ryzen MobileAMD Ryzen ThreadripperAMD Ryzen Threadripper 1000AMD Ryzen Threadripper 2000AMD Ryzen Threadripper 3000AMD Ryzen Threadripper 5000AMD Ryzen Threadripper 7000AMD Ryzen Threadripper ProAMD ZenAMD Zen 2AMD Zen 3AMD Zen 4AMD Zen+AppleApple MDual AMDDual AMD EPYCDual AMD OpteronDual Intel XeonDual Intel Xeon E5Dual Intel Xeon PlatinumIntelIntel Alder LakeIntel Amber LakeIntel Apollo LakeIntel AtomIntel Bay TrailIntel BraswellIntel BroadwellIntel Cascade LakeIntel Cascade Lake-XIntel CeleronIntel Celeron NIntel Coffee LakeIntel Comet LakeIntel CoreIntel Core 1000Intel Core 10000Intel Core 1100Intel Core 11000Intel Core 1200Intel Core 12000Intel Core 12000 MobileIntel Core 1300Intel Core 13000Intel Core 14000Intel Core 2Intel Core 2 DuoIntel Core 2 QuadIntel Core 2000Intel Core 3000Intel Core 4000Intel Core 5000Intel Core 6000Intel Core 7000Intel Core 8000Intel Core 9000Intel Core DuoIntel Core iIntel Core i3Intel Core i3-1000Intel Core i3-10000Intel Core i3-1100Intel Core i3-11000Intel Core i3-1200Intel Core i3-12000Intel Core i3-1300Intel Core i3-13000Intel Core i3-14000Intel Core i3-2000Intel Core i3-3000Intel Core i3-4000Intel Core i3-5000Intel Core i3-6000Intel Core i3-7000Intel Core i3-8000Intel Core i3-9000Intel Core i5Intel Core i5-1000Intel Core i5-10000Intel Core i5-1100Intel Core i5-11000Intel Core i5-1200Intel Core i5-12000Intel Core i5-12000 MobileIntel Core i5-1300Intel Core i5-13000Intel Core i5-14000Intel Core i5-2000Intel Core i5-3000Intel Core i5-4000Intel Core i5-5000Intel Core i5-6000Intel Core i5-7000Intel Core i5-8000Intel Core i5-9000Intel Core i7Intel Core i7 Mobile Quad CoreIntel Core i7 Quad CoreIntel Core i7-1000Intel Core i7-10000Intel Core i7-1100Intel Core i7-11000Intel Core i7-1200Intel Core i7-12000Intel Core i7-12000 MobileIntel Core i7-1300Intel Core i7-13000Intel Core i7-14000Intel Core i7-2000Intel Core i7-3000Intel Core i7-4000Intel Core i7-5000Intel Core i7-6000Intel Core i7-6000KIntel Core i7-7000Intel Core i7-7000KIntel Core i7-8000Intel Core i7-9000Intel Core i9Intel Core i9-10000Intel Core i9-11000Intel Core i9-12000Intel Core i9-12000 MobileIntel Core i9-12000KIntel Core i9-13000Intel Core i9-13000KIntel Core i9-7000Intel Core i9-8000Intel Core i9-9000Intel Core mIntel Core m3Intel Core m5Intel Core XIntel deca coreIntel Dual CoreIntel Gemini LakeIntel HaswellIntel hexa coreIntel Ice LakeIntel Ivy BridgeIntel Kaby LakeIntel LGA1150Intel LGA1151Intel LGA1200Intel LGA1700Intel LGA775Intel octa coreIntel PentiumIntel Pentium 4Intel Pentium DIntel Pentium Dual CoreIntel Pentium GoldIntel Pentium IIIntel Pentium IIIIntel Pentium Quad CoreIntel Pentium SilverIntel Quad CoreIntel Raptor LakeIntel Rocket LakeIntel Sandy BridgeIntel Sapphire RapidsIntel SkylakeIntel Skylake-XIntel Tiger LakeIntel XeonIntel Xeon BronzeIntel Xeon E-2100Intel Xeon E-2200Intel Xeon E-2300Intel Xeon E-2400Intel Xeon E3Intel Xeon E5Intel Xeon GoldIntel Xeon PlatinumIntel Xeon WIntel Xeon W-1200Intel Xeon W-1300Octa Intel XeonQuad Intel XeonProcessors groups
Comparison Table
| Key Specifications | Core i7 13700HX | Core i7 13700H |
|---|---|---|
| Vendor | Intel | Intel |
| Release Date | January 3, 2023 | January 3, 2023 |
| Device Type | Laptop | Laptop |
| Instruction Set | x86-64 | x86-64 |
| Integrated GPU | UHD Graphics (32EU) | Iris Xe Graphics (96 EU) |
| Performance Cores | 8 | 6 |
| Performance Threads | 16 | 12 |
| Base Clock | 2.1 GHz | 2.4 GHz |
| Boost Clock | 5 GHz | 5 GHz |
| Total Cores | 16 | 14 |
| Total Threads | 24 | 20 |
| L1 Cache | 80K (per core) | 80K (per core) |
| L2 Cache | 2MB (per core) | 2MB (per core) |
| L3 Cache | 30MB (shared) | 24MB (shared) |
| Fabrication Process | 10nm | 10nm |
| TDP (PL1) | 45-55 W (configurable) | 35-45 W (configurable) |
| Socket | BGA-1964 | BGA-1744 |
| GPU Base Clock | 300 MHz | 300 MHz |
| GPU Boost Clock | 1550 MHz | 1500 MHz |
| Cuda Cores | 256 | 768 |
| Execution Units | 32 | 96 |
| Memory Support | Up to 128GB | Up to 64GB |
| ECC Support | Yes | No |
| Max. Memory Channels | 2 | 2 |
Intel 13th Gen Raptor Lake Mobility CPU Lineup:
| CPU Name | Family | Cores/Threads | Base Clock | Boost Clock | GPU Cores | TDP (Base/MTP) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Core i9-13980HX | RPL-HX | 24 (8+16) | 2.2 GHz | 5.6 GHz | 32 EU | 55 / 157W |
| Core i9-13950HX | RPL-HX | 24 (8+16) | 2.2 GHz | 5.5 GHz | 32 EU | 55 / 157W |
| Core i9-13900HX | RPL-HX | 24 (8+16) | 2.2 GHz | 5.4 GHz | 32 EU | 55 / 157W |
| Core i7-13850HX | RPL-HX | 20 (8+12) | 2.1 GHz | 5.3 GHz | 32 EU | 55 / 157W |
| Core i7-13700HX | ADL-HX | 16 (8+8) | 2.1 GHz | 5.0 GHz | 32 EU | 55 / 157W |
| Core i5-13650HX | ADL-HX | 14 (6+8) | 2.6 GHz | 4.9 GHz | 16 EU | 55 / 157W |
| Core i5-13600HX | ADL-HX | 14 (6+8) | 2.6 GHz | 4.8 GHz | 32 EU | 55 / 157W |
| Core i5-13500HX | ADL-HX | 14 (6+8) | 2.5 GHz | 4.7 GHz | 16 EU | 55 / 157W |
| Core i3-13450HX | ADL-HX | 10 (6+4) | 2.4 GHz | 4.6 GHz | 16 EU | 55 / 157W |
| Core i9-13900HK | RPL-H | 14 (6+8) | 2.6 GHz | 5.4 GHz | 96 EU | 45 / 115W |
| Core i9-13905H | RPL-H | 14 (6+8) | 2.6 GHz | 5.4 GHz | 96 EU | 45 / 115W |
| Core i9-13900H | RPL-H | 14 (6+8) | 2.6 GHz | 5.4 GHz | 96 EU | 45 / 115W |
| Core i7-13800H | RPL-H | 14 (6+8) | 2.5 GHz | 4.0 GHz | 96 EU | 45 / 115W |
| Core i7-13705H | RPL-H | 14 (6+8) | 2.4 GHz | 3.7 GHz | 96 EU | 45 / 115W |
| Core i7-13700H | RPL-H | 14 (6+8) | 2.4 GHz | 3.7 GHz | 96 EU | 45 / 115W |
| Core i7-13620H | ADL-H | 10 (6+4) | 2.4 GHz | 3.6 GHz | 64 EU | 45 / 115W |
| Core i5-13600H | RPL-H | 12 (4+8) | 2.8 GHz | 4.8 GHz | 80 EU | 45 / 95W |
| Core i5-13505H | RPL-H | 12 (4+8) | 2.6 GHz | 4.7 GHz | 80 EU | 45 / 95W |
| Core i5-13500H | RPL-H | 12 (4+8) | 2.6 GHz | 4.7 GHz | 80 EU | 45 / 95W |
| Core i5-13420H | ADL-H | 8 (4+4) | 2.1 GHz | 4.6 GHz | 48 EU | 45 / 95W |
| Core i7-1370P | ADL-P | 14 (6+8) | 1.9 GHz | 5.2 GHz | 96 EU | 28 / 64W |
| Core i7-1360P | ADL-P | 12 (4+8) | 2.2 GHz | 5.0 GHz | 96 EU | 28 / 64W |
| Core i5-1350P | ADL-P | 12 (4+8) | 1.9 GHz | 4.7 GHz | 80 EU | 28 / 64W |
| Core i5-1340P | ADL-P | 12 (4+8) | 1.9 GHz | 4.6 GHz | 80 EU | 28 / 64W |
| Core i7-1365U | RPL-U | 10 (2+8) | 1.8 GHz | 5.2 GHz | 96 EU | 15 / 55W |
| Core i7-1355U | RPL-U | 10 (2+8) | 1.7 GHz | 5.0 GHz | 96 EU | 15 / 55W |
| Core i5-1345U | RPL-U | 10 (2+8) | 1.6 GHz | 4.7 GHz | 80 EU | 15 / 55W |
| Core i5-1335U | RPL-U | 10 (2+8) | 1.3 GHz | 4.6 GHz | 80 EU | 15 / 55W |
| Core i5-1334U | ADL-U | 10 (2+8) | 1.3 GHz | 4.6 GHz | 80 EU | 15 / 55W |
| Core i5-1315U | ADL-U | 6 (2+4) | 1.2 GHz | 4.5 GHz | 64 EU | 15 / 55W |
| Core i5-1305U | ADL-U | 5 (1+4) | 1.6 GHz | 4.5 GHz | 64 EU | 15 / 55W |
| Processor U300 | ADL-U | 5 (1+4) | 1.2 GHz | 4.4 GHz | 48 EU | 15 / 55W |
The laptop also housed an NVIDIA GeForce RTX 3070 Ti Laptop GPU which means that most OEM and laptop vendors will still be relying on existing GeForce RTX 30 series parts rather than waiting for NVIDIA’s next-gen RTX 40 GPUs which are expected to make a formal debut at CES 2023. A few months back, Intel announced that they will be releasing their Raptor Lake Mobile CPUs by the end of 2022. They didn’t mention if the mobile lineup will include both Raptor Lake-H and Raptor Lake-HX SKUs but it looks like we will be getting both at launch.


It is unknown what the company will pair with the new Raptor Lake mobile CPUs but with Arc GPUs mostly lining up close to the Raptor Lake CPUs, it is expected that those would be used entirely on mobile systems such as NUC and Laptops.
Frequently Asked Questions
-
The page provides a catalogue of brands and devices, each offering to view or download an updated manual. To see the entire list of Other items designed by a particular manufacturer click on ‘More’ button. Home| About| Contact 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z Home Category Other Manuals
-
As a matter of practice, quite often the usage of those goods appears to be puzzling or nearly possible. Therefore, manufacturers fit up each item with dedicated manuals & user guides which lend a helping hand whenever needed. One must admit that paper booklets are easy to lose in the piles of household stuff.
-
Upon the whole, our team is dedicated to supply you with all imaginable manuals and user guides in the most convenient way. You can search for the needed info in a variety of ways (i.e. by vendor, category, product codename) and get the desirable in a matter of seconds.
-
Which is better user guide or user guide?
To continue, user guides are helpful in installing any unit, since they give step-by-step directions on how to install correctly, for example, a monitor or a built-in lighting fixture. The other privilege of online handbooks is that they give hints on troubleshooting.
Uniwill display
Uniwill is equipped with a IPS 16.0-inches display with a resolution of 2560 x 2600 pixels and 16:10 aspect ratio. This resolution, in my opinion, is excessive for a screen of 16.0 inches. Of course, you will be pleased with the highest clarity of the screen, and, undoubtedly, it is a pleasure to use such a device. However, there is a downside – increased energy consumption, which negatively affects battery life. If the endurance of the device is more important to you, I recommend taking a closer look at configurations with a lower display resolution.
Display refresh rate is 240 Hz. This is a real gaming screen for esports players. The downside of this speed is increased power consumption. Therefore, if battery life is important to you, consider slower options. Few people will be able to feel the difference between 90 Hz and 240 Hz in everyday tasks.
The Uniwill display brightness averaged 325 nits. This is good for comfortable work indoors, perhaps outdoors on a cloudy day. In the bright sun, if I were you, I would not expect that you will be able to see anything on the screen.
Uniwill display contrast ratio is 1050:1. The contrast is good, the picture looks crisp and clear. However, in movies and games, the backlight of the screen catches the eye in dark scenes, and the picture as a whole does not look as great as on OLED panels. The screen is matte. Hit like button if you’re glossy screen fan! Subscribe to our channel if you prefer matte.
IPS displays have proven themselves very well in mobile devices, thanks to excellent viewing angles and good color reproduction at a low cost of production. Uniwill inherited the advantages of IPS panels, however, it was not without drawbacks.
Our colorimeter measurements showed 96% coverage of the color space sRGB. This is awesome, especially for games and movies, where the vivid colors is important. The Uniwill display is well calibrated by default, the gamma curve conforms to the standard, only slightly deviating from the standard, but you are unlikely to notice it with the naked eye.
The white point is noticeably shifted to the cold area. For professional use, I would recommend calibrating the display. In general, the color rendering “out of the box” is good.






![Core i7 13700hx vs core i7 13700h [benchmarks]](http://peresvet-team.ru/wp-content/uploads/7/3/e/73e8491e1833f47d007ad1841c440b7b.jpeg)







![Core i7 13700hx vs core i7 13700h [benchmarks]](http://peresvet-team.ru/wp-content/uploads/1/a/a/1aa53fe7f7fc54511174f9fd1087cb32.jpeg)







![Core i7 13700hx vs core i7 13700h [benchmarks]](http://peresvet-team.ru/wp-content/uploads/b/4/6/b46908fece20edcaa356f65607c7ebac.png)






